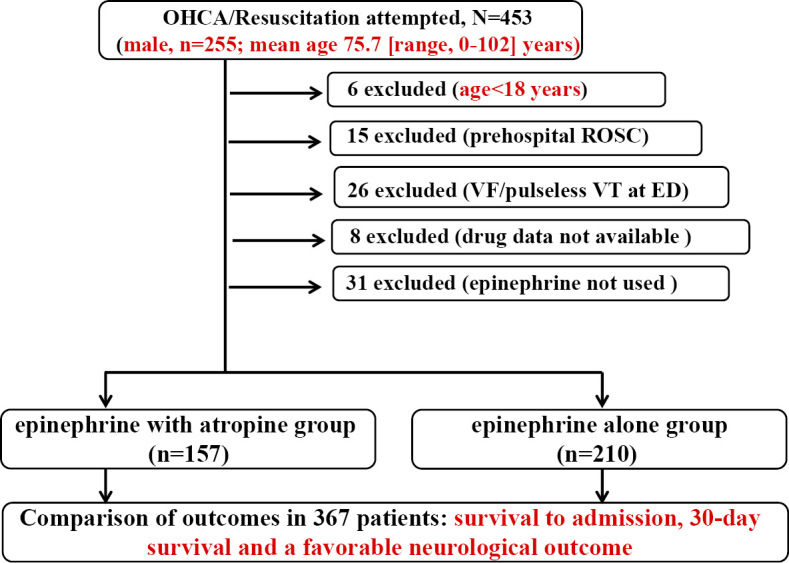
Atropine Cardiac Arrest - The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. However, several studies published in the past. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. The resuscitation council recommends that. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. The effectiveness of pharmacologic management of cardiac arrest patients is widely debated; This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between.
The effectiveness of pharmacologic management of cardiac arrest patients is widely debated; The resuscitation council recommends that. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. However, several studies published in the past. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between.
The resuscitation council recommends that. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. The effectiveness of pharmacologic management of cardiac arrest patients is widely debated; Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between. However, several studies published in the past. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic.
The Additive Effect of Atropine Sulfate during Cardiopulmonary
However, several studies published in the past. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. The resuscitation council recommends that. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between.
PPT ALS Advanced Life Support PowerPoint Presentation, free download
The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. The resuscitation council recommends that. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between. The effectiveness of.
PPT ACLS Medications PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID142073
However, several studies published in the past. The effectiveness of pharmacologic management of cardiac arrest patients is widely debated; In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex.
Part 7.2 Management of Cardiac Arrest Circulation
Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. The resuscitation council recommends that. The effectiveness of pharmacologic management of cardiac arrest patients is widely debated; In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia.
PulmCrit Epinephrine vs. atropine for bradycardic periarrest
There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. However, several studies published in the past. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation ppt download
However, several studies published in the past. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. The resuscitation council recommends that. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between.
PPT Acute coronary disorders Drugs in cardiopulmonary resuscitation
The resuscitation council recommends that. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which.
Region VIII EMS Systems February, ppt download
However, several studies published in the past. The resuscitation council recommends that. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3.
PPT ACLS Medications PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID142073
The resuscitation council recommends that. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. However, several.
Atropine for Cardiac Arrest meds.is
The resuscitation council recommends that. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest. This reflex.
However, Several Studies Published In The Past.
The resuscitation council recommends that. This reflex is reported to be a useful discriminator between. There is no evidence that the routine administration of other drugs such as atropine, calcium, sodium bicarbonate, or fibrinolytic. Assessment of the pupillary light reflex is important after cardiac arrest.
The Effectiveness Of Pharmacologic Management Of Cardiac Arrest Patients Is Widely Debated;
The recommended dose of atropine for cardiac arrest is 1 mg iv, which can be repeated every 3 to 5 minutes (maximum total. In cardiac arrest it is given to reverse asystole and severe bradycardia.