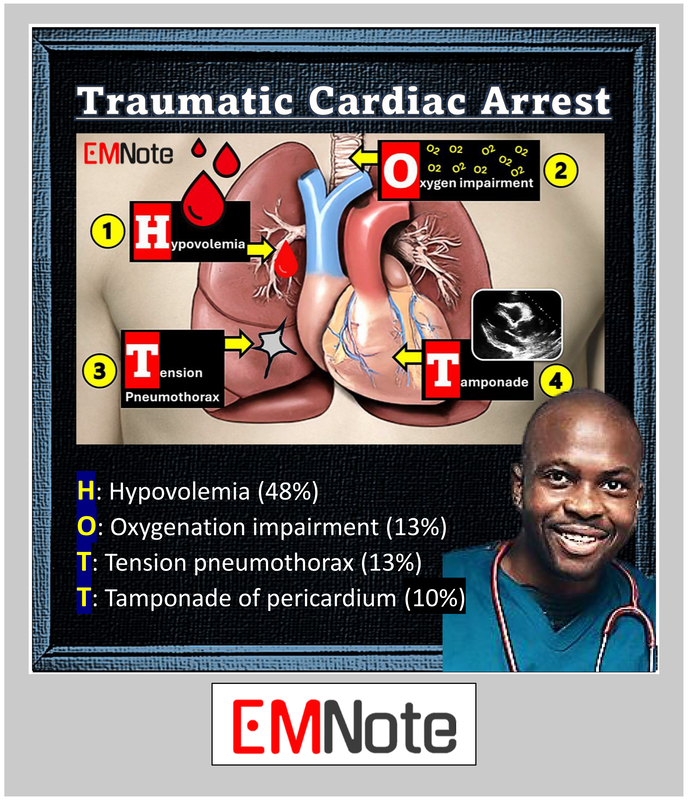
Trauma Arrest Meaning - A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful.
In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful.
A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving.
EMNote
The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving.
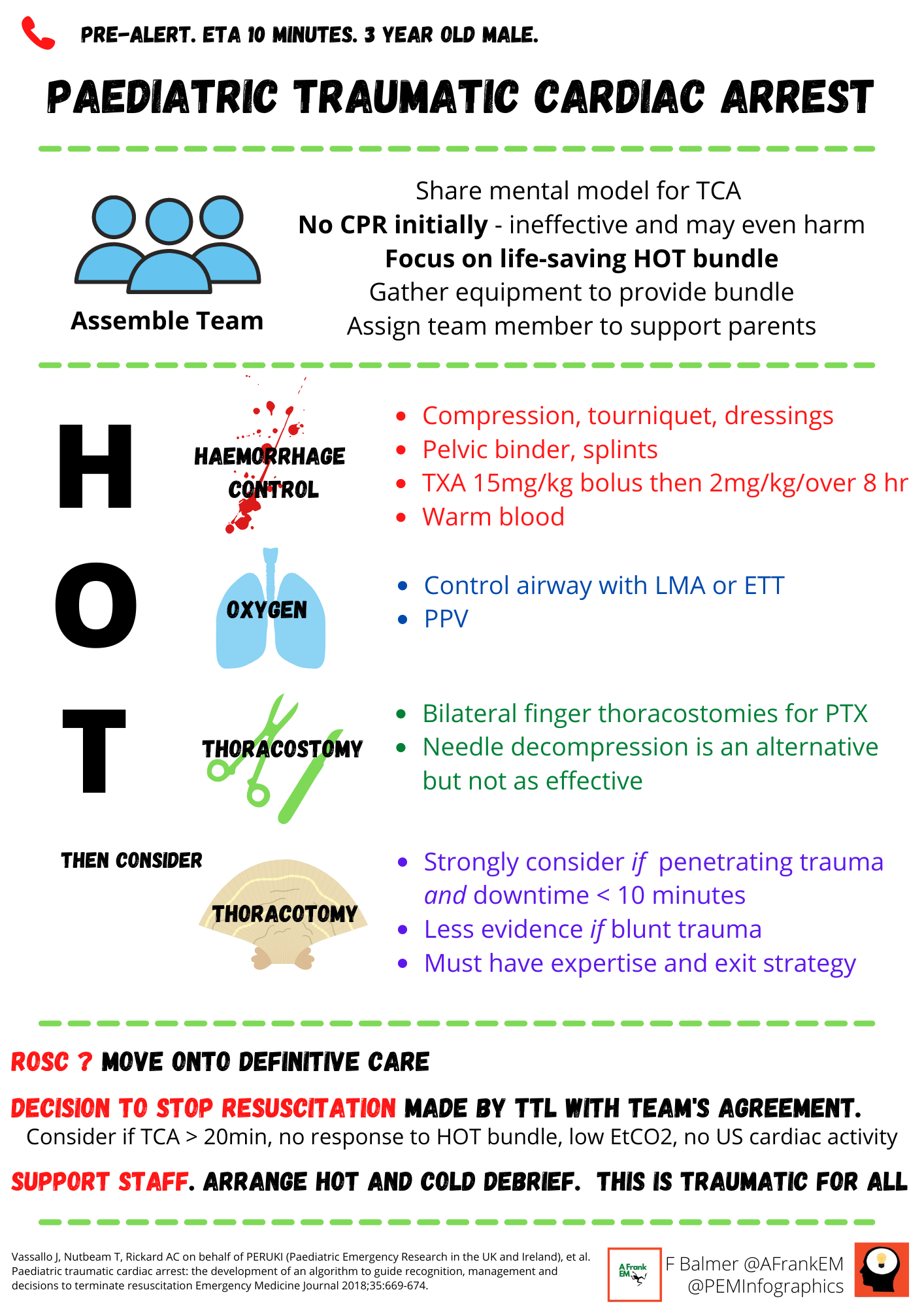
Paediatric traumatic cardiac arrest. PEM Infographics
A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving.
Chapter21 trauma arrest PPT
In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful.
CJEM Visual Abstract Just the facts traumatic cardiac arrest
In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity.
PPT Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Guidelines PowerPoint Presentation, free
In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity.
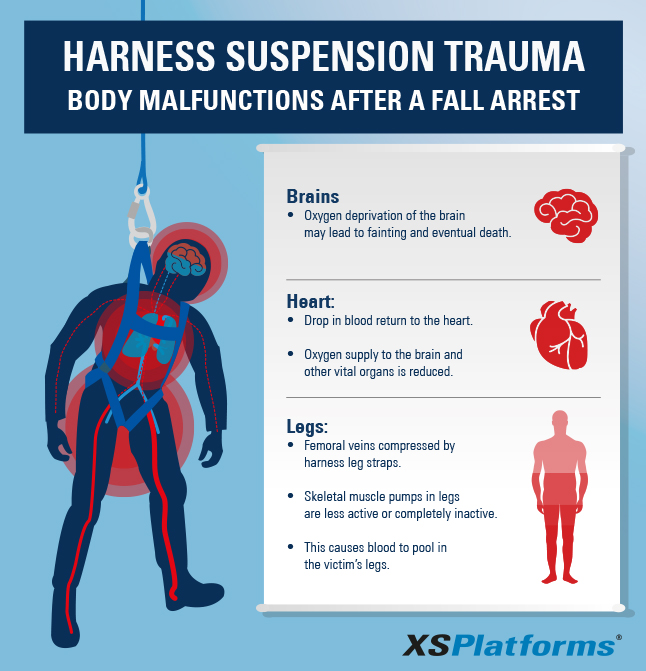
Prevent Harness Suspension Trauma after a fall arrest XSP
The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity.
Chapter21 trauma arrest PPT
The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity.
European Resuscitation Council Guidelines 2021 Cardiac arrest in
The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving.
New Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Guideline Greater Sydney Area HEMS
A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful.
Traumatic Cardiac Arrest (TCA) Maybe We Could Do Better?
A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity. In cardiac arrest due to trauma, hemorrhage control, the restoration of circulating blood volume, opening the airway, and relieving. The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful.
In Cardiac Arrest Due To Trauma, Hemorrhage Control, The Restoration Of Circulating Blood Volume, Opening The Airway, And Relieving.
The patient in cardiac arrest from a traumatic cause requires rapid assessment and treatment for any chance of meaningful. A patient who is admitted to the trauma room with no pulses or spontaneous respiratory activity.